What Is a CMS? Learn How to Manage Website Content Effectively
CMS enables easy creation, management, and publishing of content without coding, streamlining workflows, saving time and costs, and enhancing user experience.
13/08/2025
loading...
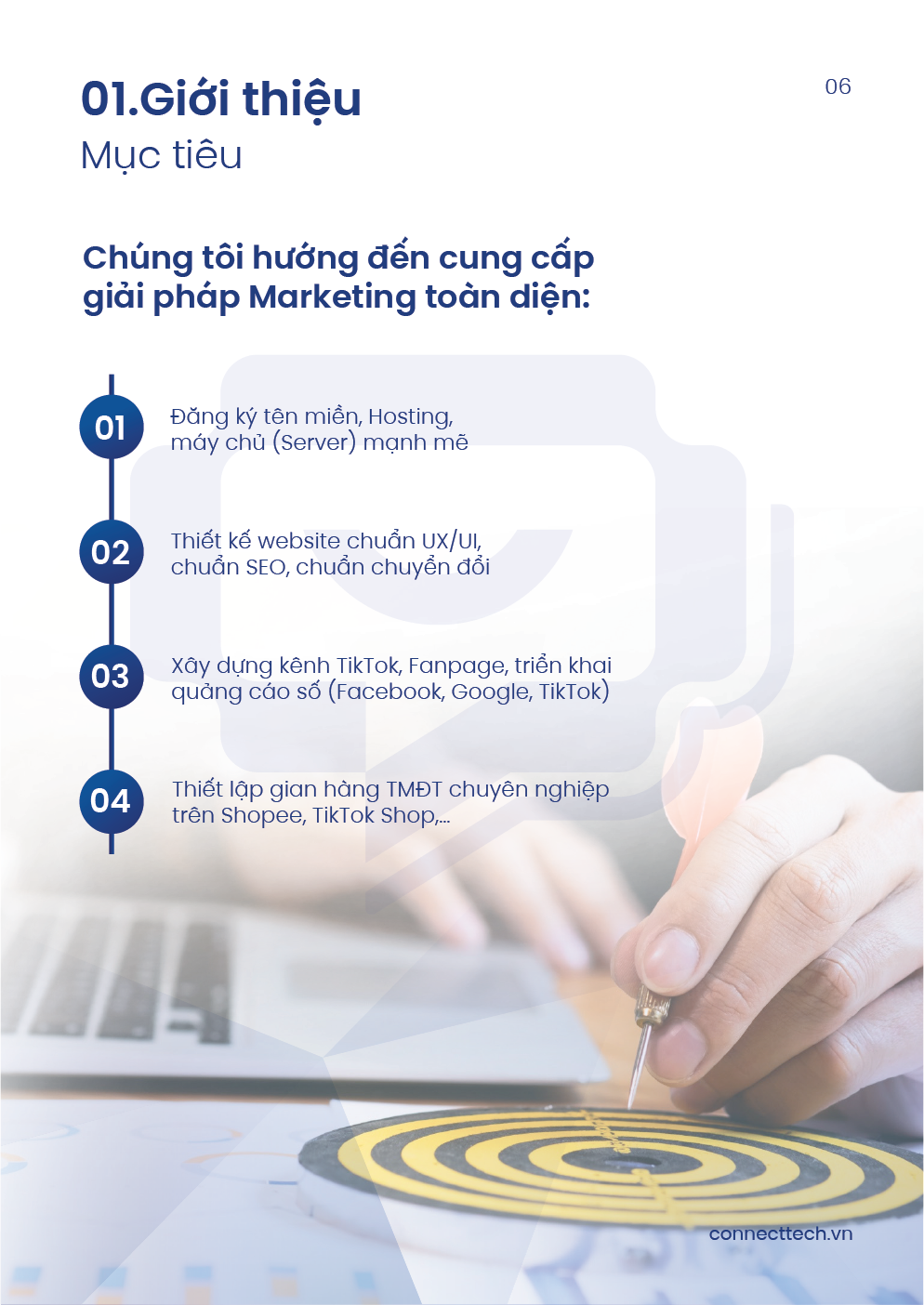
CMS (Content Management System) is a tool that enables quick creation, editing, organization, and publishing of content without requiring programming knowledge. It helps save time, reduce costs, streamline workflows, and enhance user experience. But the question is: How do you choose and use a CMS effectively to meet your content management needs? This article will help you understand how to select and maximize the efficiency of a CMS system that suits your content strategy.
I. What Is a CMS?
A CMS (Content Management System) is a content management platform that allows users to easily create, edit, organize, and distribute digital content without needing advanced programming skills. It simplifies website administration and is suitable for both individuals and businesses.

Typically, a CMS consists of two main components:
- CMA (Content Management Application) – Provides a user-friendly interface for drafting, editing, publishing, and previewing content before it goes live.
- CDA (Content Delivery Application) – Processes and displays the created content on websites or other digital channels.
The role of a CMS goes beyond internal content management; it also acts as a bridge between businesses and customers, ensuring a consistent, multichannel content experience and optimizing communication effectiveness.
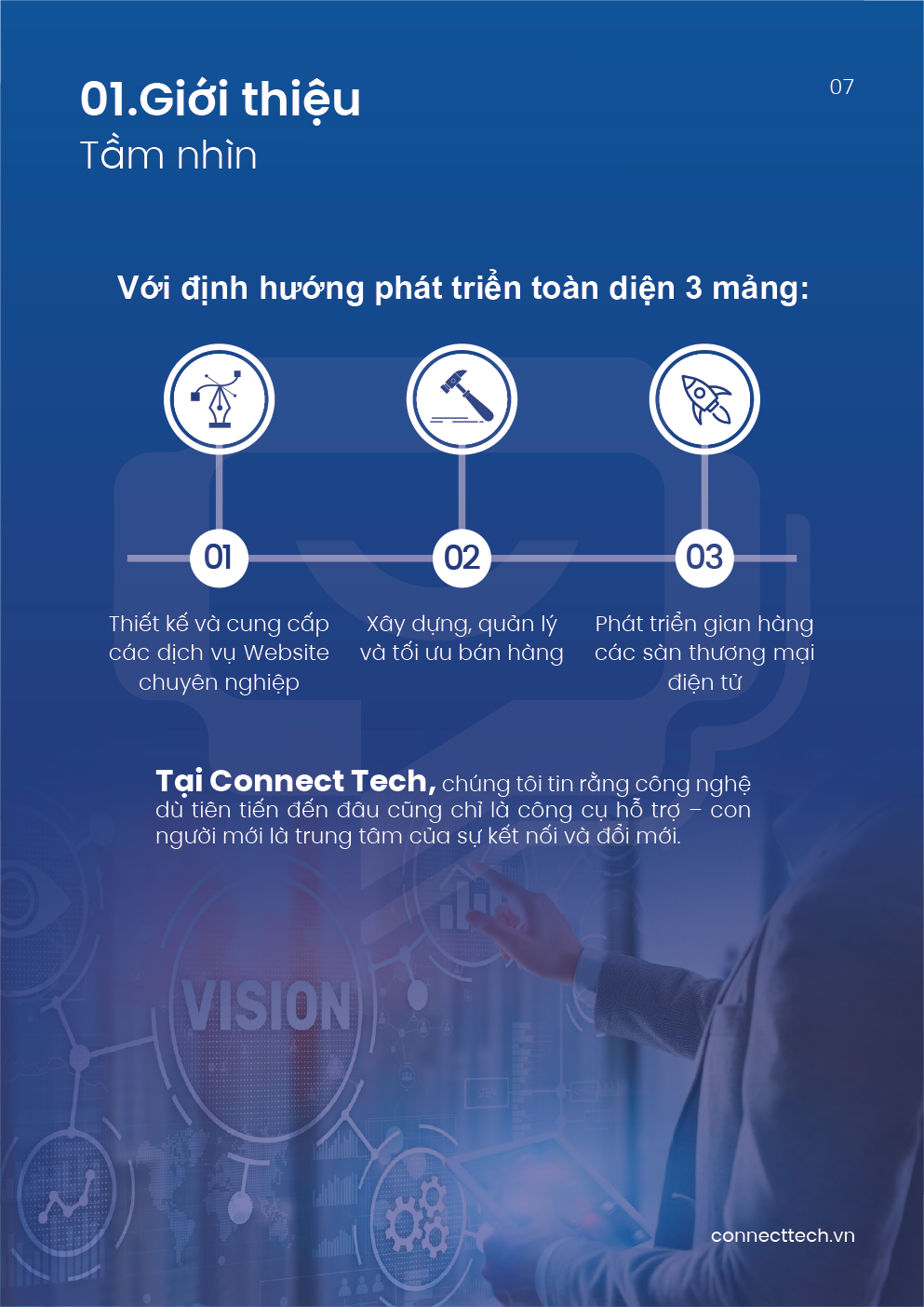
II. How Does a CMS Work?
The core principle of a CMS lies in separating content from presentation. This means content is stored independently in a database, while the visual layout (template/interface) is designed separately. When users access the site, the CMS merges these elements to generate a complete webpage.
Here’s how it typically works:
- Content creators log into the CMS and use the CMA to draft or edit content.
- The content is stored in a database and can be previewed for accuracy.
- Upon clicking “publish,” the CDA processes the content, applies the selected template, and displays it on the website or other digital platforms.

Examples of CMS types based on functionality:
- Traditional CMS: Combines content and presentation in one system (e.g., WordPress, Joomla).
- Hybrid CMS: Offers flexibility with both traditional display and API-based distribution.
- Headless CMS: Manages content only and delivers it via API, allowing display across multiple platforms (websites, apps, IoT devices).
III. Key Features of a CMS
1. SEO Support
Most CMS platforms come with built-in or add-on SEO tools to improve website visibility on search engines. Key features include:
- Optimized URL structures for better rankings
- Customizable meta tags (title, description)
- XML sitemap generation for faster indexing
- Schema markup support for enhanced search result displays
- Page speed optimization to improve user experience and SEO scores

2. System Integration
Modern CMS platforms are designed to integrate seamlessly with other systems such as CRM, e-commerce solutions, DAM (Digital Asset Management), and analytics tools like Google Analytics. These integrations help synchronize data, reduce manual tasks, and optimize operational workflows.
3. Content Management
CMS allows users to easily create, edit, categorize, and tag content systematically. All data is stored centrally with version control mechanisms, enabling content recovery when needed. This ensures logical organization, consistency, and ease of search and retrieval.
4. E-commerce
Many CMS platforms include e-commerce modules that support product management, shopping carts, order processing, and online payments. This transforms a website into a complete online store without needing a separate platform.

5. Workflow & User Permissions
A major strength of CMS is its ability to assign user roles such as admin, editor, or contributor. It also supports multi-step content approval workflows before publishing, ensuring quality, accuracy, and compliance with editorial standards—especially important for organizations with large content volumes and multiple managers.
6. Multilingual Support
CMS makes managing multiple language versions of a website simple and consistent. This is especially useful for businesses operating in multiple countries or serving diverse audiences. The system allows centralized translation, editing, and updates, saving time and reducing errors.
7. Data Analytics & Content Personalization
Many CMS platforms integrate content analytics tools to track traffic, engagement rates, and user behavior. Some systems also offer content personalization features, recommending articles or products based on individual preferences and behavior—enhancing user experience and conversion rates.

8. A/B Testing
A/B testing features in CMS allow comparison between different versions of content, images, or layouts. This helps businesses choose the most effective option based on real data before full deployment, reducing risks and improving campaign performance.
IV. Popular Types of CMS
1. Open Source CMS
These platforms have publicly available source code that can be freely used, modified, and distributed. Examples include WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal. Open source CMS is usually free, highly flexible, and supported by large user communities. However, to fully utilize its capabilities, administrators may need technical expertise, especially for deep customization.
2. Custom-Coded CMS / Framework-Based
These systems are built from scratch or based on frameworks, offering maximum customization and high performance—ideal for projects with specific requirements. Downsides include longer development time, higher costs, and the need for experienced developers for maintenance and upgrades.

3. Commercial (Paid) CMS
These are CMS platforms developed and offered by software companies as turnkey solutions, such as Wix, Squarespace, or Weebly. They are user-friendly, offer good technical support, and come with many built-in features. However, users must pay monthly or annual fees, and customization options are often limited compared to open source CMS.
V. Considerations When Choosing and Using a CMS
Before selecting a CMS, businesses should evaluate several factors to ensure long-term effectiveness:
Content Governance: Determine whether your organization has policies and workflows for content creation, editing, and management. A suitable CMS should support the implementation and enforcement of these processes.

Information Architecture & Tagging: Content should be clearly categorized and tagged for easy search and comprehension by both internal teams and end users.
Content Management Workflows: The CMS should allow standardization and automation of workflows—from creation and approval to publishing—reducing manual effort and minimizing errors.
User Experience for Content Access: Consider how stakeholders, from internal staff to customers, search for and access information. A good CMS should offer fast search, intuitive interfaces, and clear content presentation.
Technology & Applications: Assess whether current technologies are fully utilized. If not, consider upgrades or new systems to streamline information flow and ensure security. Cloud-based CMS solutions can offer flexibility and anytime access.
Business Value of CMS: The chosen CMS should enable efficient and secure content and data management while meeting legal and regulatory requirements. Its true value lies in helping businesses optimize workflows, save time, and improve productivity.

VI. Conclusion
A CMS is not just a content publishing tool, it’s a strategic platform that helps businesses streamline operations, enhance user experience, and maintain brand consistency across all channels. Choosing the right CMS based on your needs, scale, resources, and growth direction will bring long-term benefits—from cost and time savings to increased revenue.
In today’s competitive landscape, a suitable CMS empowers you to manage and maximize the value of your content, turning your website into a powerful business tool. Start by assessing your organization’s needs, experimenting with options, and investing in the CMS solution that fits best.
Read more: What is Content Marketing? A Beginner’s Guide
Relate News
Keyword rankings and key factors that determine SEO success
Improving keyword rankings drives more traffic to your website, strengthens credibility, and optimizes conversions through SEO strategies and supporting tools.
View moreShopee Permanent Account Lock: Causes and Effective Solutions
Understand the causes, signs, and how to handle Shopee permanent account locks, helping protect your rights and avoid losing data, revenue, and reputation.
View moreTotal Online Marketing Services: Comprehensive Solutions For Businesses
Comprehensive online marketing services help businesses build their brand, reach target customers, optimize costs, boost sales, and maintain a competitive edge
View moreProfessional & Effective Restaurant Marketing Service Provider
Restaurant marketing services help build a professional brand, attract customers, optimize online channels and ads, and deliver truly stable revenue for F&B.
View moreWhat is Link Juice? Its Role and How It Works in Off-Page SEO
page that receives a high amount of quality Link Juice will have a greater chance of ranking higher on Google while building strong trust in the eyes of users
View moreWhat is a Brand Archetype? Its role in branding strategy
Brand Archetype helps a brand truly define a clear personality, effectively connect with customers, build trust, and stand out in a highly competitive market.
View moreWhat is Omnichannel Marketing? Benefits and Practical Strategies
Omnichannel marketing helps businesses reach customers comprehensively, boost revenue, and build a strong, effective brand presence across multiple platforms.
View moreWhat is the <a> tag in HTML? How to use it with detailed examples
Explore the <a> tag in HTML, an essential bridge for creating links and guiding users smoothly between pages, with examples, uses, and SEO optimization tips.
View moreWhat is DeepSeek? Explore the powerful AI platform from China.
DeepSeek is an AI platform from China, powerful and cost-efficient, supporting NLP, programming, data analysis, and directly competing with GPT and Gemini.
View moreWhat is Google Gemini? Meet Google's new AI assistant
Google Gemini is Google's new generation AI tool, integrating Google services, supporting learning, work, and creativity with outstanding intelligent thinking.
View moreInstructions on how to cancel purchases on Lazada quickly and effectively
Detailed instructions on how to cancel orders on Lazada according to each status, with important notes to help you handle it quickly, avoid trouble and save time.
View moreWhat is Copilot? Microsoft's intelligent AI assistant helps you work more efficiently
Copilot is an intelligent AI assistant from Microsoft, designed to help users optimize their daily work, improve productivity, and manage their time efficiently
View more